Introduction
The Indian economy, like a giant jigsaw puzzle, consists of various pieces that come together to create a vibrant and complex picture. Let’s break down the basics of the Indian economy in simple terms.

1. What is the Indian Economy?
The Indian economy refers to the system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services in India. It’s like a bustling marketplace where people buy and sell things, and the government plays a role in overseeing and managing this entire process.

2. Key Sectors: Agriculture, Industry, and Services
Imagine the economy as three main pillars. The first pillar is agriculture, which involves farming and producing crops. The second pillar is industry, which includes manufacturing things like cars, gadgets, and clothing. The third pillar is services, which covers areas like banking, education, healthcare, and tourism.

3. GDP – The Big Picture Number
GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, is a big number that tells us how much the entire country produces in a year. It’s like adding up the value of all the goods and services made in India. When GDP is growing, it means the country’s economy is getting bigger.
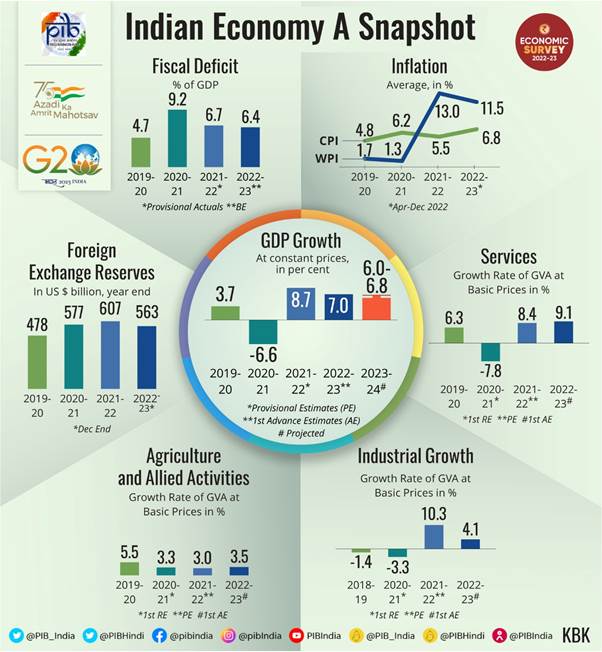
4. Inflation – The Rising Prices
Have you noticed how the price of chocolates or toys sometimes goes up? That’s inflation. It’s like when everything gets a little more expensive over time. It’s usually okay as long as it doesn’t rise too fast, because high inflation can make things tough for people.
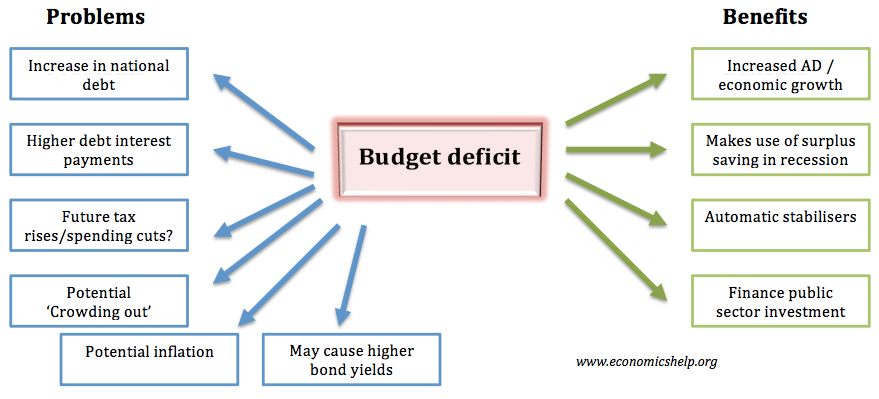
5. Budget and Deficit – Managing Money
Just like you get pocket money, the government also has money. They collect taxes from people and companies. The government’s budget is like a plan for how much money they will spend on things like schools, roads, and hospitals. If they spend more than they earn, it’s called a budget deficit.
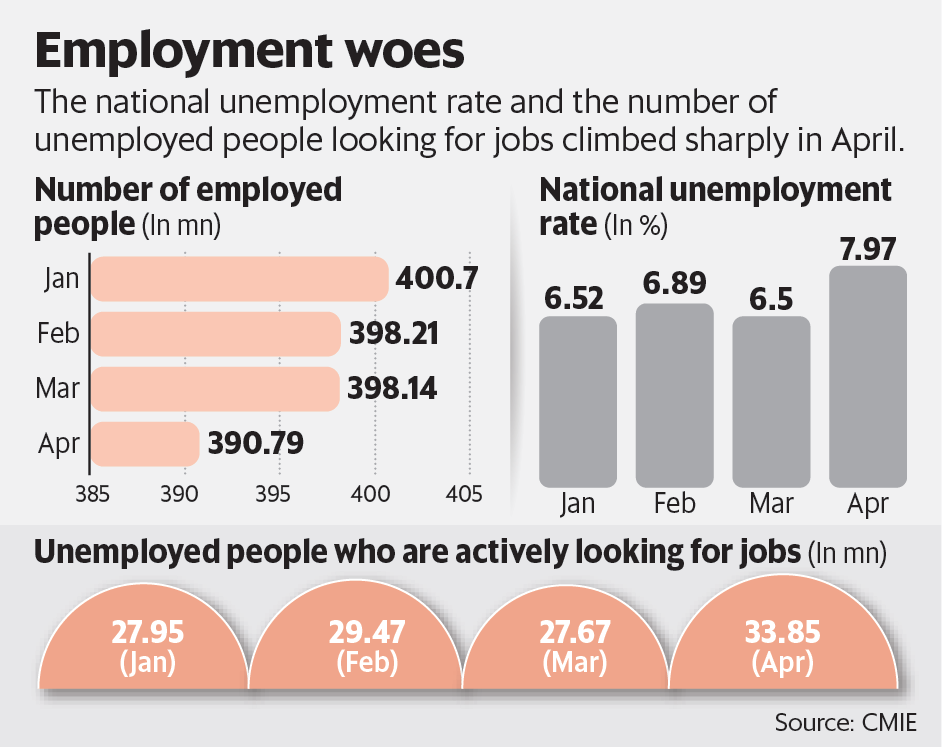
6. Jobs and Unemployment
Think of the economy as a big job fair. When companies are doing well, they hire more people. But sometimes, companies struggle and might let people go. When lots of people are looking for jobs and can’t find any, it’s called unemployment.
7. Foreign Trade – Buying and Selling with Other Countries
India also trades with other countries. It sells things like spices, clothes, and software to them, and buys things like electronics, machinery, and oil. This is called international trade, and it’s important for the economy.
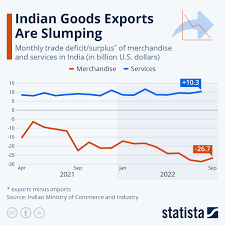
8. Challenges and Opportunities
The Indian economy faces challenges like poverty, unequal distribution of wealth, and environmental issues. But it also has opportunities, like a huge young population and a growing technology sector.
In a nutshell, the Indian economy is a mix of people producing, buying, and selling goods and services. It’s like a complex puzzle, but understanding its basic pieces can help us grasp how it all fits together to create a thriving nation.
Also read :-Understanding Diabetes: A Simple Guide
1 Comment
Pingback: Chandrayaan-3: A Stellar Success in Exploring the Moon - Zarsco Blogs🚀