Introduction: What is Spatial Computing?
Spatial computing is a technology that blends the digital and physical worlds. It allows computers to understand and interact with the real environment using tools like cameras, sensors, and artificial intelligence. This creates experiences where digital content feels like a natural part of our surroundings.
Key Features of Spatial Computing
- 3D Interaction: Engage with digital objects in three dimensions, making interactions more immersive.
- Real-Time Mapping: Devices can map and understand the physical environment instantly.
- Natural Controls: Use gestures, voice commands, and eye movements to control digital elements.
- Blended Reality: Combine virtual and real-world elements seamlessly.
Applications of Spatial Computing
1. Healthcare
Doctors use spatial computing for surgeries, training, and patient care. For example, surgeons can view 3D models of organs during operations, improving precision.
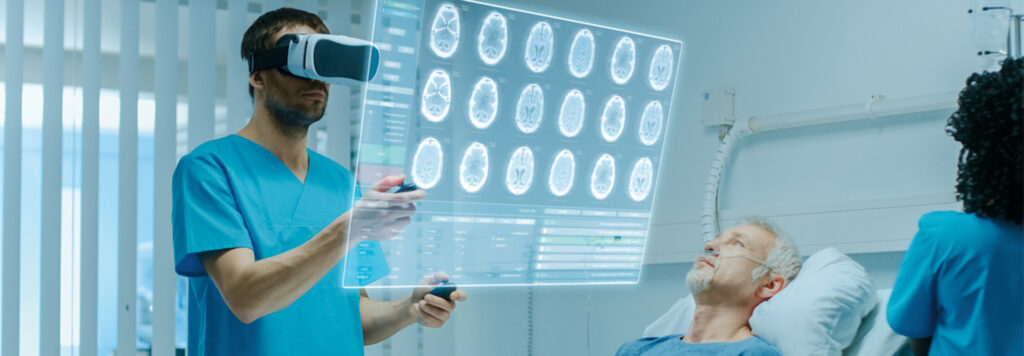
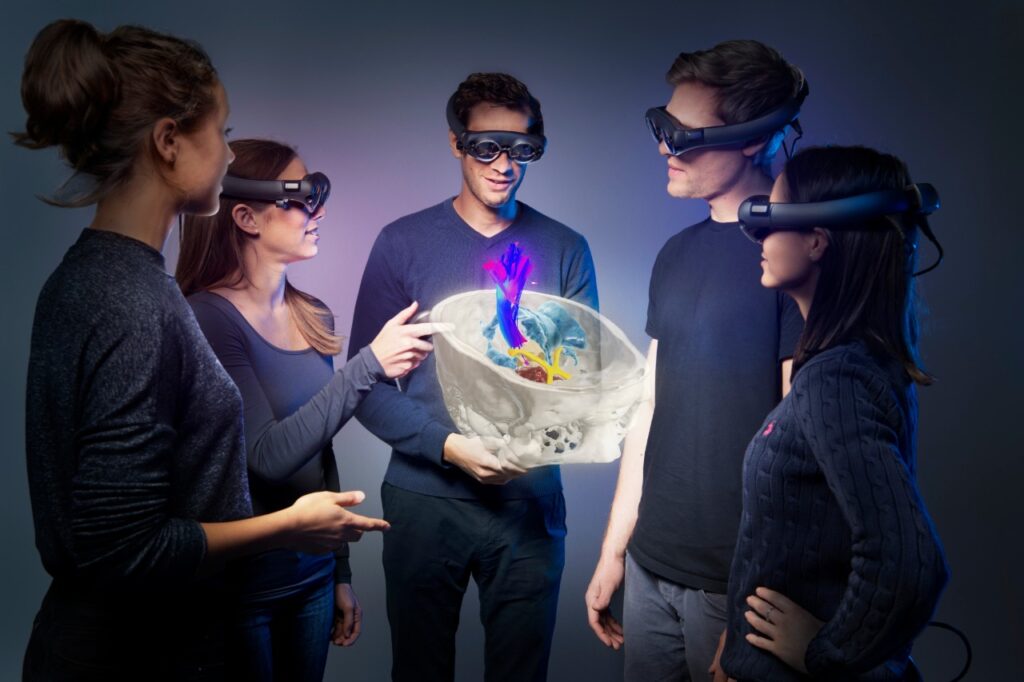
2. Education and Training
Students and professionals can learn through interactive simulations. Medical students might practice procedures in a virtual environment, enhancing their skills safely.

3. Manufacturing and Design
Engineers and designers can visualize products in 3D before building them. This helps in identifying issues early and improving designs efficiently.

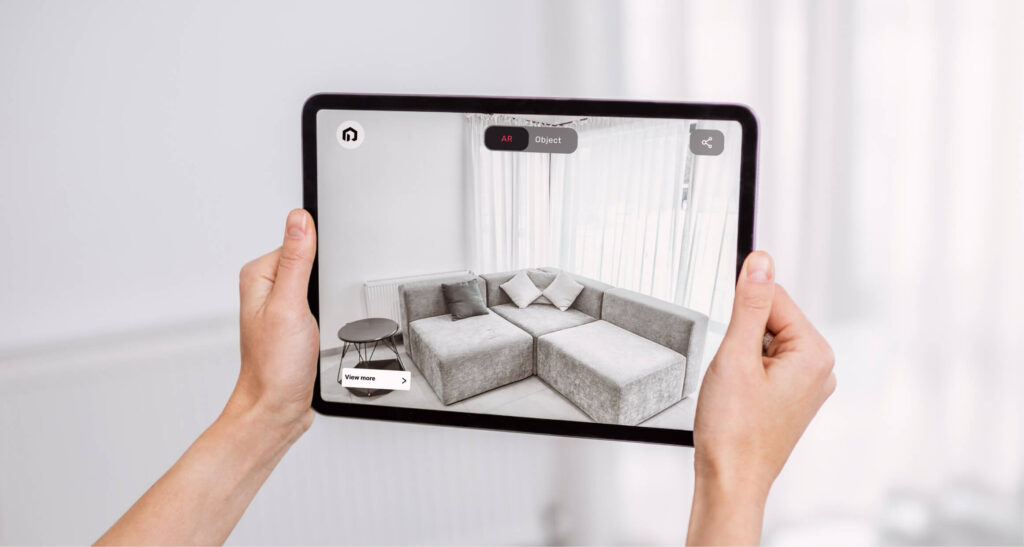
4. Retail and Shopping
Customers can try products virtually. For instance, using AR apps to see how furniture fits in their homes before purchasing.

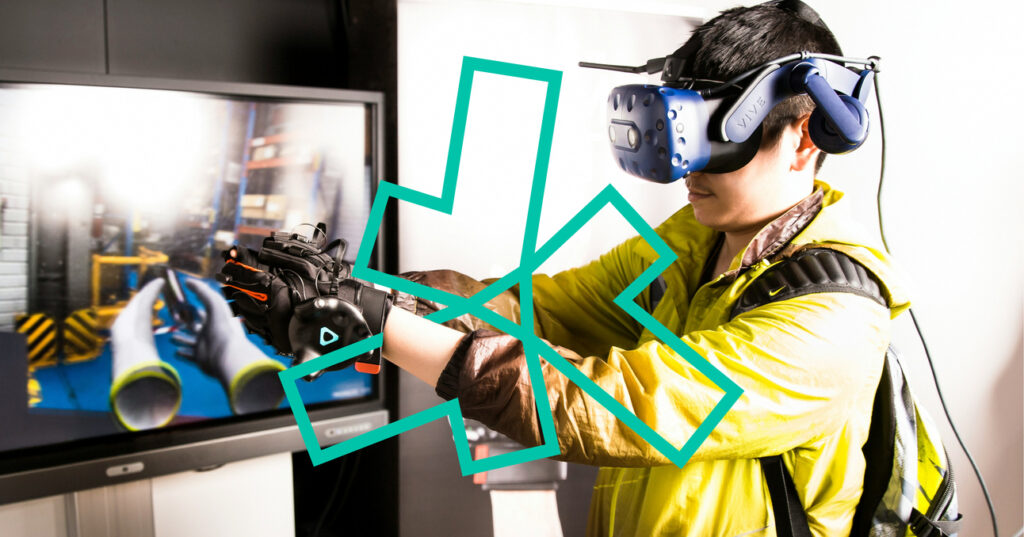
5. Entertainment and Gaming
Games and media become more engaging with spatial computing. Players can interact with virtual elements in their real environment, enhancing the gaming experience.

Impact on Daily Life
Spatial computing is changing how we work, learn, and play. It makes tasks more interactive and efficient. As devices become more affordable and user-friendly, more people will experience these benefits in their daily routines.
Challenges Ahead
- Cost: High prices of devices can limit accessibility.
- Privacy: Collecting environmental data raises concerns about user privacy.
- Technical Limitations: Battery life and device comfort need improvements for prolonged use.
Conclusion
Spatial computing is a transformative technology bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds. Its applications across various sectors are enhancing experiences and efficiency. As the technology evolves, it holds the promise of becoming an integral part of our everyday lives
Also read :Deforestation and Its Impact: A Deep Dive into Environmental Consequences
